CDS/CDL & CANCER
The Anticancer Potential of Chlorine Dioxide in Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells
Abstract
Background
Chlorine dioxide (ClO2) is an effective disinfectant consisting of oxygen, chloride, and potassium. Because of its high oxidative capacity, ClO2 exerts antimicrobial, antiviral, and antifungal effects. However, its anticancer effects remain to be elucidated.
Results
Our preliminary findings showed that LTSCD (long-term stabilized ClO2 solution) significantly inhibited the proliferation of SCLC (small-cell lung cancer) cells (p < 0.01) with less toxicity in HUVEC cells. Additionally, LTSCD induced apoptotic cell death in SCLC cells through nuclear blebbing and vacuolar formation. However, LTSCD treatment did not induce cell cycle arrest in both cell lines.
Conclusions
LTSCD (LTSCD: long-term stabilized ClO2 solution) can be a therapeutic potential for the treatment of SCLC (small-cell lung cancer). However, further investigations are required to assess the LTSCD-induced cell death in SCLC both in vitro and in vivo.
Aqueous chlorine dioxide (ClO2) is an effective disinfectant and a water purifier and is used in mouth rinses and surface disinfectants. ClO2 consists of oxygen, chloride, and potassium, and its action depends on the release of nascent oxygen during the action. Therefore, ClO2 exerts high oxidative capacity and biocidal activity, making it a non-toxic, antimicrobial, antiviral, and antifungal agent. ClO2 accelerates wound healing, especially burns, by inducing cyclic GMP production through the induction of the guanylate cyclase enzyme [5-7]. However, few studies have investigated the anticancer activity of ClO2 in cancer treatment [8,9].
Indeed, ClO2 potentially inhibits the proliferation of cancer cells by inducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production.
In the study by Schwartz (2017), ClO2 treatment reduced the intracellular pH of cancer cells and improved two patient (pancreas and prostate cancer) outcomes [8]. [ https://www.cancertreatmentjournal.com/articles/chlorine-dioxide-as-a-possible-adjunct-to-metabolic-treatment.html Chlorine dioxide as a possible adjunct to metabolic treatment (cancertreatmentjournal.com)]
Additionally, Kim et al. (2016) reported that ClO2 inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells as well as LoVo, HCT-116, and SW-480 colon cancer cells via the production of ROS [9]. [http://koreascience.or.kr/article/JAKO201611639306040.page Anticancer and Antiviral Activity of Chlorine Dioxide by Its Induction of the Reactive Oxygen Species -Journal of Applied Biological Chemistry | Korea Science]
Recent studies have shown that ClO2 prevents the recombinant spike protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 by attaching to its receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 [12,13]. Additionally, ClO2 interacts with one or more cysteine, tyrosine, or tryptophan amino acid residues of the spike proteins in enveloped viruses and also attaches to the viral DNA of non-enveloped viruses [14,15].
Furthermore, CIO2 interacts with aromatic amino acids and leads to the oxidization of the proteins, and binds to DNA or RNA [19,20].
In this context, Kim et al. (2016) evaluated the antiviral and anticancer effects of CIO2 and reported that CIO2 significantly inhibits breast and colon cancer cell proliferation due to possibly inducing ROS [9]. Another possible mechanism of CIO2-induced cytotoxicity is that CIO2 can oxidize polyamines, and these oxidative molecules, hydrogen peroxide and aldehydes, are extremely toxic to cancer cells. Furthermore, the increased hydrogen peroxide generated by oxidation can induce apoptosis, pyknosis, and necrosis. Therefore, CIO2-mediated oxidation causes cell death of cancer cells by endogenous hydrogen peroxide [21,22]. In our study, we showed that LTSCD considerably inhibited the proliferation of DMS114 cells with less toxicity in HUVEC cells. Additionally, LTSCD induced apoptosis with nuclear blebbing and G2/M arrest in DMS114 cells. However, dose-dependent G2/M arrest slightly increased in DMS114 cells. The oxidative stress and elevated ROS level induce the DNA damage response, leading to cell cycle arrest and causing apoptotic cell death [23]. However, imbalanced ROS levels and DNA damage overwhelm the DNA damage repair mechanism and cause exit from the cell cycle. Therefore, excessive damage leads to the exit cell cycle without triggering the cell cycle checkpoints and develops resistance despite apoptosis [23,24]. Therefore, further investigations should be conducted to elucidate the underlying mechanism of LTSCD-induced apoptosis and its association with the cell cycle.
…
This study has some limitations. This is the first study evaluating CIO2 efficacy in SCLC cells. Therefore, we did not compare its effect with any other chemotherapeutic drug. Second, we did not evaluate the underlying molecular mechanisms of LTSCD-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Therefore, we designed this study as preliminary research, and further investigations are needed to assess the anticancer activity of LTSCD in different types of cancer in line with these novel findings.
https://www.cancertreatmentjournal.com/articles/chlorine-dioxide-as-a-possible-adjunct-to-metabolic-treatment.html Chlorine dioxide as a possible adjunct to metabolic treatment
Abstract
A first patient with metastatic adenocarcinoma of the pancreas has decided, on his own, to refuse chemotherapy but to treat himself with lipoïc acid, hydroxycitrate combined with oral ingestion of chlorine dioxide.
His blood tests and radiological examinations have almost normalized and the disease is stable at 18 months.
Another patient with hormone resistant metastatic prostate cancer has experienced a sharp drop in PSA level as well as improved medical condition. From extensive literature review, the mechanism of action of chlorine dioxide is unknown. It is our hypothesis (albeit unproven) that chlorine dioxide results in tumor cell acidification of the alkaline pH of cancer cells.
Introduction: Cancer is a fermentation process
In the early 1920’s Otto Warburg demonstrated a unique feature of cancer cells, namely an increased uptake of glucose and secretion of lactic acid by cancer cells, even in the presence of oxygen (e.g. the aerobic glycolytic phenotype)1,2. This aerobic fermentation is the signature of cancer3. Warburg also noticed a concomitant decreased number of mitochondria (grana),sup>4.
…
One other crucial consequences of the mitochondrial defect is intracellular alkalosis7. Tumors show a 'reversed' pH gradient with a constitutively increased intracellular pH that is higher than the extracellular pH. This gradient enables cancer progression by promoting proliferation, the evasion of apoptosis, metabolic adaptation, migration, and invasion12–15.
There is evidence that an acidic extracellular pH promotes invasiveness and metastatic behaviour in several tumor models14,16, proteolytic enzyme activation and matrix destruction17–19.
In normal cells, the intracellular pH (pHi) oscillates during the cell cycle between 6.8 and 7.37. The oscillation of the pH during the cell cycle matches the value of the decompaction of the histones, RNA polymerase activation, DNA polymerase activation and DNA compaction before mitosis7,11.
The intracellular pH of the cancer cells has been less studied. During the cell cycle, it oscillates between 7.2 and 7.5. Intracellular alkalosis is probably a consequence of the decreased oxidative phosphorylation resulting in decreased secretion of carbon dioxide (CO2) and the CO2 reacts with water to create carbonic acid. Cell transformation or enhanced cancer cell division and resistance to chemotherapy are all associated with a more alkaline pHi20–23.
The Warburg effect may be a direct consequence of the activation of oncogenes6. Infection by an oncogenic virus or exposure to a carcinogen inhibits the mitochondrial function and causes the Warburg’s effect24–29.
Reversing the Warburg inhibits tumor growth
The introduction of normal mitochondria into cancer cells restores mitochondrial function, inhibits cancer cell growth and reverses chemoresistance30-35. Also the fusion of cancer cells with normal mitochondria results in increased ATP synthesis, oxygen consumption and respiratory chain activities together with marked decreases in cancer growth, resistance to anti-cancer drugs, invasion, colony formation in soft agar, and « in vivo » tumor growth in nude mice31.
As the Warburg aerobic glycolytic phenotype and its effects on metabolism are key to cancer, the obvious question is whether drugs can be designed to target it. To alleviate the Warburg effect, pyruvate should be converted into Acetyl-CoA, which would decrease the bottleneck that results in the activation of both the Pentose Phosphate Pathway and the glutaminolysis. The mitochondrial yield should be increased to stimulate the synthesis of CO2 and the increased secretion of CO2 would result in a decreased intracellular alkalosis.
The combination of α-lipoïc acid and hydroxycitrate36–39 has been reported to slow cancer growth, in murine xenografts. This inhibition appears to be independent of the primary tumor site and has been reproduced in different laboratories40,41.
The most likely mechanism of action for α-lipoïc acid in its reduction of tumor growth is the inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (the same target of Dichloroacetic acid (DCA)). This enzyme inhibits the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase and is known to be up-regulated in cancer cells expressing the Warburg aerobic glycolytic phenotype. Pyruvate dehydrogenase catalyses the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA, the initial step of the final conversion of glucose to carbon dioxide and water in the TCA cycle, with the concomitant production of ATP. Therefore, it is reasonable to suggest that blocking the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase will at least partially restore the activity of pyruvate dehydrogenase, thereby increasing the flux of pyruvate through the TCA cycle in the mitochondria, while simultaneously reducing the production of lactic acid and most importantly decreasing the flux in the pentose pathway shunt9.
There are several reports of metabolic treatment utilizing a combination of α-lipoïc acid and hydroxycitrate together with conventional cancer therapy. Starting in January 2013, metabolic treatment (α-lipoïc acid/hydroxycitrate with low doses of chemotherapy plus Naltrexone) was offered to patients sent home after the failure of conventional cytotoxic chemotherapy for metastatic cancer (irrespective of the primary site) but with a Karnovsky performance status above 70 (quantification cancer patients' general well-being and activities of daily life)42–46. Of the first randomly selected eleven patients, five were alive and reasonably well 30 months after the start of treatment43-45.
In the update of a subsequent study, patients with multiple brain metastasis (n=4) or glioblastoma (n=6) were treated with a combination of conventional and metabolic treatments (α-lipoïc acid/hydroxycitrate) as well as ketogenic diet. Five out of six patients with glioblastoma were alive and stable after two years, while two of the four patients with multiple brain metastases are alive and well three years later46,47.
Cases reports:
Patient number 1
The first case is a 65 year old French gentleman with biopsy-proven unresectable well differentiated adenocarcinoma of the pancreas in June 2016 . The cholestasis was treated by a derivation in December 2016 which was effective in alleviating the obstruction. The tumor markers (CA 19-9 and CEA) were uninformative. The patient subsequently refused chemotherapy and decided by himself to start a treatment involving
1) Ketogenic diet
2) Lipoïc acid 800 mg twice a day and hydroxycitrate 500mg three times a day
3) Chlorine dioxide up to 32 drops per day. Chlorine dioxide was produced by the activation of NaCLO2 by 4% HCl. The activation time takes 3mn and a drop contains around 86 micromoles of CLO2 if the activation is total.
As of 9/2017, the patient was living normally, the blood tests were normal, the tumor mass such as seen on CT scan had grown from 3 to 5 cm. No side effects were noted. There was ne concomitant chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Patient number 2
Having heard of the first case, a second patient started a similar treatment. He is a 67-year-old man. He was diagnosed in 8/16 with Gleason 8 adenocarcinoma of the prostate responsible of a cord compression that was successfully treated by laminectomy and post op radiationtherapy. At the start of disease PSA was 1320. Degarelix was started in 8/16 with concomitant ketogenic diet. Because of partial responds chemotherapy with Docetaxel (150mg IV) was started in December 2016. Chemotherapy was discontinued after two cycles because of poor tolerance. Simultaneously, starting In mid November metabolic treatment with lipoïc acid as well as hydroxycitrate. He performs weekly assessment of his PSA.
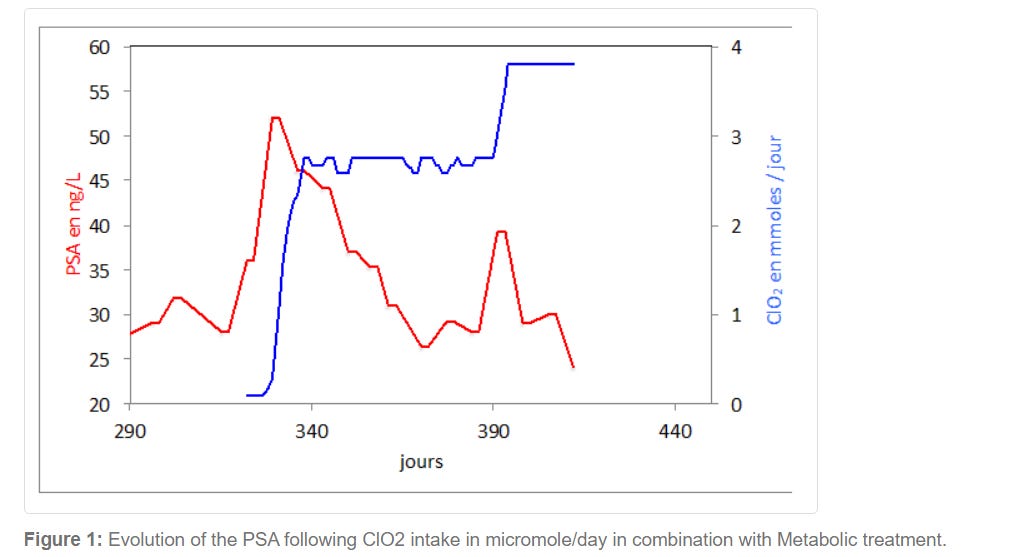
End of march, the PSA had dropped to 27 and stayed at this value up to beginning of June, but started increasing, in three weeks from 27 to 52 (figure 1). Metastatic pain increased and was responsible of Karnovsky of 70. At that stage the patient started to take chloride dioxide. The PSA dropped linearly for eight weeks to 26. The patient took eight times a day, 344 micromoles of chlorine dioxide. After these eight weeks of decrease, the PSA started to increase in three weeks from 26 to 39. At that stage, metastatic pain, which has almost completely disappeared, was responsible of insomnia. He started to take chlorine dioxide drops not only during the daytime but also every 90 minutes at night.
Nightly metastatic pain decreased drastically from day one, and the second part of the night was practically pain free. The PSA decreased again linearly from 39 to 24.
Discussion and conclusion:
Chlorine dioxide is a poorly studied chemical entity. The mechanism of action of ClO2 is poorly understood. It is our hypothesis that chlorine dioxide decreased the intracellular pH. We are currently running experiments to confirm/infirm this hypothesis. Correcting the intracellular pH may be an alternative or an adjunct to a metabolic treatment as there is extensive literature that many effective cancer treatments decrease the intracellular pH (pHi)2,23,47: literature on increased survival support for the combined use of antacids (which prevent proton extrusion from the tumour cells) with standard chemotherapy15,48–50.
Today, cancer is thought to be a set of very complex diseases with thousands of different mutations. That apparent complexity has led to personalized medicine. However, modern biology has confirmed the universality of the Warburg aerobic glycolytic phenotype. Furthermore, the fact that the combination of α-lipoïc acid and hydroxycitrate slows down cancer growth in every tumor model studied to date suggests that at least some targets are the same in a large spectrum of tumors.
It is possible that the addition of chlorine dioxide increases the response to metabolic treatment.
http://koreascience.or.kr/article/JAKO201611639306040.page Anticancer and Antiviral Activity of Chlorine Dioxide by Its Induction of the Reactive Oxygen Species -Journal of Applied Biological Chemistry | Korea Science
이산화염소의 활성산소 생성 유도에 의한 항암 및 항바이러스 활성
Abstract
Chlorine dioxide has been used for a disinfectant by exhibiting antimicrobial activity and is also potent to kill insect pests infesting stored grains. This study aimed to extend the usefulness of chlorine dioxide with respect to anticancer and antiviral activities. Cytotoxicity of chlorine dioxide was assessed against five different human cancer cell lines. Chlorine dioxide exhibited significant cytotoxicity against two breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7, MDA-MB-231) and three colorectal cancer cell lines (LoVo, HCT-116, SW-480). This cytotoxicity appeared to be associated with the capacity of chlorine dioxide to induce the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Compared to control insect cell lines, the cancer cell lines possessed much higher levels of ROS. On the other hand, a treatment of an antioxidant, vitamin E, significantly reduced the cytotoxicity, suggesting that the cytotoxicity was induced by high levels of ROS production. Chlorine dioxide exhibited antiviral activity against different viruses. A baculovirus, Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcNPV), is a dsDNA insect virus and lost its viral activity to form polyhedral viral particles in response to chlorine dioxide. The antiviral activity against AcNPV was dependent on the incubation time with chlorine dioxide. Tobacco mosaic virus is a ssRNA plant virus and was reduced in its population after exposure to chlorine dioxide along with significant decrease of viral symptoms. These results indicate that chlorine dioxide possesses anticancer and antiviral activities probably due to its inducing activity of ROS production.


Im not certain of exactly what you are talking about here other than ClO2 chlorine dioxide being nearly a silver bullet in our health maintenance, especially when almost nothing else will successfully kill cancer cells.
Thank you for this essay Outraged Human along with all your other fine work!
I have used it for literally years and it is my go to. First I was using MMS which is the 2 bottle system and now I use CDS which is much easier on the stomach. I swear by this stuff, it has been my lifesaver many a time and it has kept me away from the white coat system. No wonder they tried to ban it and jailed people over this. Why because it will give you the freedom you deserve to heal yourself and stay away from the system. Something they certainly do not want and that is independence away from their death system. Please read up on using it before jumping headlong into using it. More is not better with this stuff, it is small doses first. Know what your body can tolerate, do not create a healing crisis. For those who are scared to use it internally please learn about all the other protocols where it is used externally for a myriad of problems. I also use it to fix myself when I get bio resonance shedding from one who has obviously taken the jibby jabs and has weaponized their energy field. These people make me really ill, incapacitated ill if I get hit too hard. I have commented about it in detail on substack here. Look on telegram to learn more about MMS/CDS and the protocols etc and testimonies, everywhere else they are censored big time.