Why do I agree with Dr. Andrew Moulden?
If you cut off blood supply and oxygen to the heart it is very painful… It is called heart attack.
Lack of oxygen to tissue is very very painful…
A heart attack (stroke of the heart) occurs when the blood flow that brings oxygen to the heart muscle is reduced or cut off.
Autism is just a tip of an iceberg…
If you are a parent of an autistic child, please stand up
WHAT CAN REDUCE OR CUT OFF BLOOD FLOW?
WHAT ABOUT VACCINE TOXICITY AND OXIDATIVE STRESS?
LET'S QUOTE SOME OF THE THOUSANDS OF SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES:
HARVARD:
https://web.archive.org/web/20220130154141/https://web.math.princeton.edu/~sswang/developmental-diaschisis-references/Herbert%20-%20brain%20enlargement.pdf Large Brains in Autism: The Challenge of Pervasive Abnormality
The Neuroscientist, Volume 11, Number 5, 2000
Neuro-inflammation, oxidative stress & microglia damage found in autistic brain tissue.
“Chronic disease or external environmental sources” (ie, heavy metals) may be the cause.
Oxidative stress, brain inflammation, and microgliosis has been much documented in association with heavy metal exposures.
It also appears that accompanying these neuroinflammatory findings are signs of oxidative damage (C. Pardo, personal communication, November 2004), signs of which are also being discerned in studies of autistic brain tissue by other investigators (Perry and others 2005), as well as in peripheral tissue samples (Chauhan and others 2004; James and others 2004).
A further possibility is that neuroinflammation and associated increased oxidative stress could alter the chemical milieu of the brain, leading, for example, to increased excitotoxicity that in turn would increase cortical arousal.
Now, additional consideration needs to be given to the possible roles played by metabolic alterations of inflammation and oxidative stress, the as yet unidentified drivers of these metabolic alterations, and the extent to which microglial and astroglial activation and inflammatory cytokines and chemokines might alter both brain structure and brain function.
… persistent inflammation and oxidative stress could over time lead to impaired cell health or apoptosis.
Oxidative stress, brain inflammation, and microgliosis have been much documented in association with toxic exposures including various heavy metals, pesticides, and air pollution (Kim and others 2002; Zurich and others 2002; Campbell 2004; Ling and others 2004; Shanker and others 2004; Filipov and others 2005).
For instance, the pathophysiologies of inflammation, oxidative stress, and excitotoxicity are greatly linked, and it appears these types of mechanisms are implicated in the brain as well as in some of the sensory and sleep regulation, epilepsy, immune, and gastrointestinal complaints commonly seen in autism.
Inflammation, oxidative stress, excitotoxicity, and other neurochemical changes and their triggers open a range of possibilities for research into potential treatment targets.
IOWA STATE UNIVERSITY:
https://web.archive.org/web/20041022080002/http://www.bb.iastate.edu:80/~jat/glutchp.pdf OXIDATIVE STRESS INCLUDING GLUTATHIONE, A PEPTIDE FOR CELLULAR DEFENSE AGAINST OXIDATIVE STRESS
Oxygen is the primary oxidant in metabolic reactions designed to obtain energy from the oxidation of a variety of organic molecules. Oxidative stress results from the metabolic reactions that use oxygen, and it has been defined as a disturbance in the equilibrium status of prooxidant/anti-oxidant systems in intact cells. This definition of oxidative stress implies that cells have intact pro-oxidant/antioxidant systems that continuously generate and detoxify oxidants during normal aerobic metabolism.
When additional oxidative events occur, the pro-oxidant systems outbalance the anti-oxidant, potentially producing oxidative damage to lipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, ultimately leading to cell death in severe oxidative stress.
Mild, chronic oxidative stress may alter the anti-oxidant systems by inducing or repressing proteins that participate in these systems, and by depleting cellular stores of anti-oxidant materials such as glutathione and vitamin E.
A disturbance in pro-oxidant/anti-oxidant systems results from a myriad of different oxidative challenges, including radiation, metabolism of environmental pollutants and administered drugs (these are xenobiotics, i.e., foreign materials), and immune system response to disease or infection.
The immune response is especially interesting since many toxic oxidative materials are generated in order to kill invading organisms. Evidence for the role of a variety of chemicals called radicals in these processes has led to interest in the reactions of partially reduced oxygen products and radical and non-radical species derived from them. A variety of reactive nitrogen species derived from the reactions of nitric oxide play important roles as well. A radical species is specifically understood to be any atom that contains one or more orbital electrons with unpaired spin states. The radical may be a small gas molecule such as oxygen or nitric oxide, or it may be a part of a large biomolecule such as a protein, carbohydrate, lipid, or nucleic acid. Some radical species are very reactive with other biomolecules and others like the normal triplet state of molecular oxygen are relatively inert.
Oxidative stress has been implicated in human disease by a growing body of facts.
Many dietary constituents are important sources of protective agents that range from anti-oxidant vitamins and minerals to food additives that might enhance the action of natural anti-oxidants. Indeed, at least part of the beneficial effects of a high fruit and vegetable diet is thought to derive from the variety of plant anti-oxidants that might act as beneficial supplements in humans.
On the other hand, materials such as
pesticides, polyunsaturated lipids, and a variety of plant and microorganism-derived toxins might produce pro-oxidant effects in man.
Glutathione is a peptide found in most every cell at a high concentration.
Its unique features include a) high water solubility, permitting cells to use high concentrations of the peptide, b) an amino acid constituent (cysteine) that is readily oxidized and reduced under the mild conditions required in cell metabolism, and c) an unusual peptide bond that prevents nonspecific destruction by hydrolytic enzymes that attack normal peptide bonds.
Proteins have many reactive sites that can be damaged during oxidative stress, but interest has centered on three measurable events. First, aggressive radicals such as hydroxyl radical can fragment proteins in plasma, and the fragmented products of specific proteins, if known, can be detected.
Second, proteins may contain metal binding sites that are especially susceptible to oxidative events through interaction with the metals. These reactions usually produce irreversible modifications in amino acids that might be involved in metal ion binding, e.g., histidine. These modifications may produce signal sequences that are recognized by specific cellular proteases that degrade such proteins. Finally, many intracellular proteins have "reactive" sulfhydryls groups on specific cysteine residues (See ANTI-OXIDANTS) that can be modified (oxidized) to specific forms (disulfides) that can be reduced again by metabolic processes. Similarly, some proteins have a "reactive" methionine that can undergo a reversible modification to methionine sulfoxide (Figure 6b). The disulfide and sulfoxide forms of these two amino acids may actually serve a protective role, since the metabolic reversibility of the protein modification effectually detoxifies the oxidative species that caused the modification. The reversible nature of the modifications of cysteine and methionine also suggests that oxidative modifications of this type may have a role in regulating metabolic events in the cells under oxidative stress.
CELLULAR ANTI-OXIDANTS
The most effective anti-oxidant in oxidative stress is dependent on the specific molecules causing the stress, i.e., superoxide anion, lipid peroxides, iron-generated hydroxyl radical, etc., and the cellular or extracellular location of the source of these molecules. As an example, damage to a cell membrane occurs from both internally and externally generated oxidative stress. This damage is most effectively prevented by vitamin E which reacts with peroxyl and hydroxyl radicals, carotenoids which react with singlet oxygen, and possibly by membrane bound proteins. The chain-breaking anti-oxidant function of vitamin E in membranes results from its close association with polyunsaturated components of the membrane. It can be regenerated by reaction with cytoplasmic vitamin C and glutathione, or by membrane-bound quinols. Vitamin C is subsequently reduced by glutathione through the glutathione cycle that is described below. Thus, a specific attack on membranes results in the participation of at least three different anti-oxidants. Similarly, when oxidative stress occurs in plasma a variety of different anti-oxidants participate in the response.
THE GLUTATHIONE REDOX CYCLE AND THE PROTEIN S-THIOLATION CYCLE
The low molecular weight thiol, glutathione, and "reactive" protein sulfhydryls (exposed cysteines in many proteins) are primary participants in cellular anti-oxidant systems. Glutathione is abundant (3 to 10 mM) in cytoplasm, nuclei, and mitochondria and is the major soluble antioxidant in these cell compartments. Reactive protein sulfhydryls are abundant in both soluble proteins and in membrane-bound proteins.
Glutathione is oxidized by hydrogen peroxide to glutathione disulfide by the selenium-containing enzyme, glutathione peroxidase, and also by other enzymes that may use lipid peroxides rather than hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant. Thus, glutathione can detoxify both soluble and lipid peroxides.
The concentration of cellular glutathione has a major effect on its anti-oxidant function and it varies considerably as a result of nutrient limitation, exercise, and oxidative stress. Under oxidative conditions, the concentration of glutathione can be considerably diminished through conjugation to xenobiotics, and by secretion of both the glutathione conjugates and glutathione disulfide from the affected cells.
https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/pdf/10.1146/annurev-biochem-061516-045037 Oxidative Stress
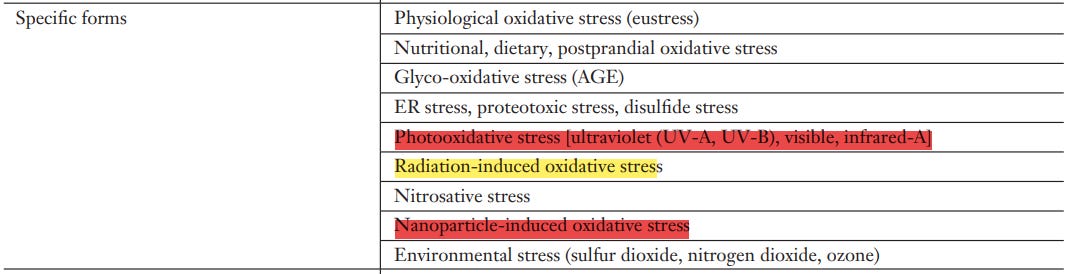
Nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress
👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆
PHOTOOXIDATIVE STRESS
Photoexcitation of endogenous or exogenous sensitizer molecules (photosensitization) leads to formation of reactive species, notably singlet molecular oxygen, electronically excited carbonyls, and superoxide anion radicals; these may cause molecular damage. The wavelength ranges of biological importance are ultraviolet B and ultraviolet A, but visible light and even infrared-A are also known to generate photobiological responses.
Dietary micronutrients such as carotenoids and polyphenols can provide nutritional protection against damage from sunlight. Of the carotenoids, lycopene has the highest rate constant in the reaction with singlet molecular oxygen.
REDOX MEDICINE
Approaches Increasing Oxidative Stress (Therapeutic Prooxidants)
Approaches Decreasing Oxidative Stress (Therapeutic Antioxidants)
Nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jpssuppl/93/0/93_1-P-003/_pdf Oxidative stress-mediated neural cell death induced by nanoparticles
https://bmcpharmacoltoxicol.biomedcentral.com/track/pdf/10.1186/s40360-018-0256-8.pdf Hesperidin alleviates zinc oxide nanoparticle induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress
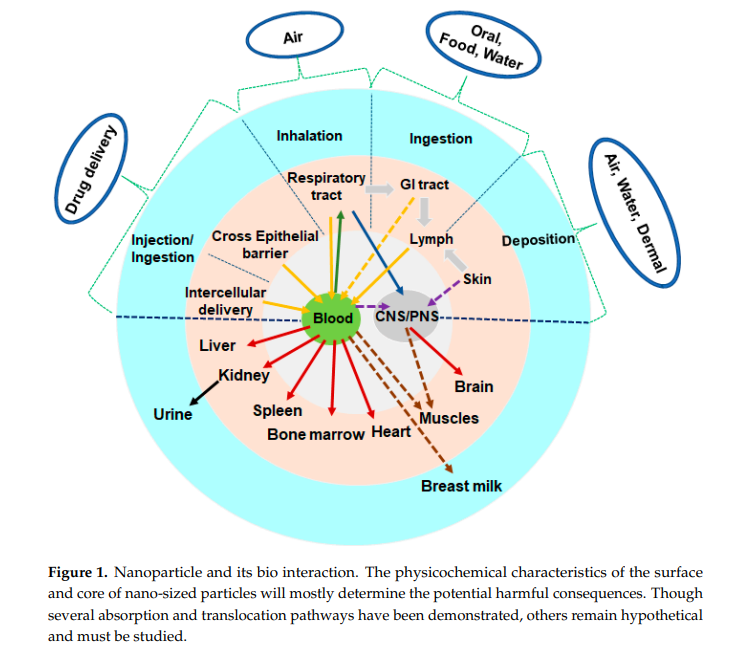
However, nano size particles can cause toxicity, because they are highly reactive and cause oxidative stress in human and animals as they can enter the circulation and reach to different organs of the body.
Nanoparticles can cause oxidative stress and can lead to damage in protein structures and cause mutations. Repetitive exposure to nZnO can induce DNA damage in human nasal mucosa and cause potential toxicity, including cytotoxic, genotoxic, and proinflammatory response.
Titanium dioxide exposure can lead to toxicity and cellular responses of intestinal cells. They may then translocate to blood causing adverse biological reactions in different tissues. The adverse effects of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on the male reproductive tract, in particular spermatogenesis, and suggest that selenium can protect against AgNP-induced testicular toxicity.
Flavonoids are one of the most important antioxidants in fruits and vegetables, especially in the genus Citrus, as they provide health benefits through cell signaling pathways and antioxidant effects.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study shows that HSP (hesperidin) decreases liver toxicity in rats and that its effect is mediated by antioxidant activities. Results in this study suggest that HSP helps in reducing the hepatotoxicity of nZnO as also indicated by protection of histopathological changes in tissue.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4574116/pdf/13578_2015_Article_46.pdf Zinc ferrite nanoparticle-induced cytotoxicity and oxidative stress in different human cells
The Nano Particles have high possibility to deposit in the respiratory system and can retain in the lungs for a long time where they provoke oxidative stress and an inflammatory burden with respect to their fine-sized equivalents. On the other hand, liver is a primary site of NPs accumulation after they get entry to circulatory system. Studies suggest that NPs get absorbed as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract and distributed different vital organs including liver via the circulatory system. Therefore, we have selected human lung (A549), skin (A431) and liver (HepG2) cell lines to explore cytotoxic response of zinc ferrite NPs.
The underlying mechanisms of toxicity of NPs are not fully explored. One mechanism more often argued is the induction of oxidative damage of cell macromolecules, either due to the reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation or by inactivation of antioxidant defense system. ROS generation is a crucial factor not only in apoptotic pathway, but also in genetic damage, inflammation and several other cellular processes . Our earlier studies have shown that magnetic NPs have potential to induce ROS mediated cytotoxicity in different human cells. In the present study, we investigated the cytotoxicity and oxidative stress response of zinc ferrite NPs in three different types of human cells.
Zinc ferrite nanoparticles reduced the cell viability
Zinc ferrite nanoparticle‑induced membrane damage
Zinc ferrite nanoparticle‑reduced glutathione level
Zinc ferrite nanoparticle‑induced reactive oxygen species generation
Zinc ferrite nanoparticle‑reduced mitochondrial membrane potential
Zinc ferrite nanoparticle‑altered the expression of apoptotic genes
Zinc ferrite nanoparticle‑ induced cytotoxicity through ROS generation
Cytotoxicity of zinc ferrite NPs was effectively abolished N-acetyl-cysteine (ROS scavenger) indicating that oxidative stress might be one of the possible causes of zinc ferrite NPs toxicity.
👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆❗❗❗❗👆👆👆👆
https://www.hal.inserm.fr/inserm-00617214/document Cytotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by different metallic nanoparticles on human kidney cells
http://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/42f5/e17f5520316fea8005674ea2c2faf8bf40b2.pdf Oxidative stress mediated apoptosis induced by nickel ferrite nanoparticles in cultured A549 cells
Due to the interesting magnetic and electrical properties with good chemical and thermal stabilities, nickel ferrite nanoparticles are being utilized in many applications including magnetic resonance imaging, drug delivery and hyperthermia. Recent studies have shown that nickel ferrite nanoparticles produce cytotoxicity in mammalian cells.
Nickel ferrite nanoparticles were also found to induce oxidative stress evidenced by generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and depletion of antioxidant glutathione (GSH).
Further, co-treatment with the antioxidant l-ascorbic acid mitigated the ROS generation and GSH depletion due to nickel ferrite nanoparticles suggesting the potential mechanism of oxidative stress.
https://mdpi-res.com/d_attachment/antioxidants/antioxidants-12-00703/article_deploy/antioxidants-12-00703-v2.pdf?version=1678768446 Metal-Based Nanoparticles and Their Relevant Consequences on Cytotoxicity Cascade and Induced Oxidative Stress, Antioxidants 2023, 12, 703
Despite the promise that nanotechnology will improve our lives, the potential risks of technology remain largely uncertain.
The degree of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidative stress caused by material nanoparticles (NPs) depends on many factors, such as size, shape, chemical composition, etc. These characteristics enable NPs to enter cells and interact with biological macromolecules and cell organelles, resulting in oxidative damage, an inflammatory response, the development of mitochondrial dysfunction, damage to genetic material, or cytotoxic effects.
Nevertheless, more than ~2800 commercial nanoparticulate-based applications are promptly available. These NPs exhibit specific physicochemical characteristics and are manufactured for applications in biological and commercial functions, including cancer research, drug delivery, cosmetics, biosensors, environmental remediation, antimicrobial agents, and environmental remediation.
These engineered mNPs-altered physicochemical and structural characteristics may cause various material interactions and toxicological consequences. Transition metals, including Fe, Ni, Cu, and Cr, may be absorbed into the surface of mNPs due to their enormous specific surface area and catalyze Fenton reactions that directly damage DNA, which may lead to carcinoma.
Since oxidative stress is a significant factor in NP-induced injury, it can result in a variety of physiopathologic effects, including genotoxicity, necrosis, inflammation, fibrosis, metaplasia, hypertrophy, lipid peroxidation, damage to macromolecules such as DNA, leading to mutations, and fostering the growth of tumors.
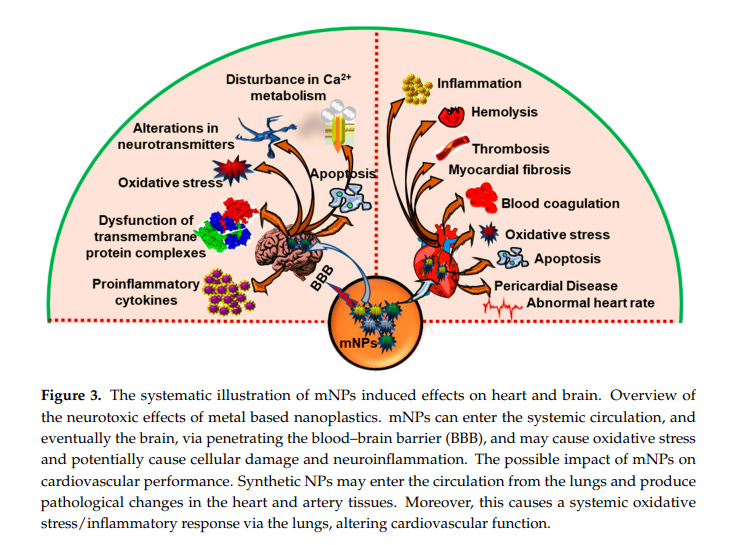
According to a study by Kan et al., there are three potential mechanisms for adverse effects on the cardiovascular system:
(a) synthetic NPs may travel from the lungs to the bloodstream and cause pathological alterations in the tissue of the heart and arteries;
(b) engineered NPs may cause a systemic oxidative stress/inflammatory reaction through the lungs that changes cardiovascular function; or
(c) they could affect cardiovascular performance through the neurogenic pathway.
Several mNPs have been demonstrated to cause hepatic steatosis due to residual NPs in the liver. Despite the fact that 30–99% of specified NPs will accumulate and sequester in the liver, the accumulation of specific mNPs in the liver has been observed to induce oxidative stressors, which in turn disrupt the liver’s metabolism and homeostasis.
The kidneys are essential organs that filter all hazardous chemicals and metabolites through urine. Nonetheless, the key diseases that contribute to kidney disorders are oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and necrosis.
Environmental factors such as air pollution can cause oxidative damage in the brain, which may result in neurodegenerative illnesses. NPs disrupt the tight junctions of the blood–brain barrier or enter the central nervous system (CNS), allowing them to access and induce neurotoxicity…
MASKS? PCR “TESTS”? Nano masks are face masks made with nanoparticle fabric. Nanoparticles made from various materials such as gold, carbon, silver, etc., enable RT-PCR…
https://www.rescuepost.com/files/dc-2009.ppt
Hannah Poling Concession
November 9, 2007
Hannah met all milestones in first 18 months. At 9 months: Mimicking sounds, crawling, and sitting.
At 12-month pediatric visit: Saying “Mom” & “Dad,” pulling self up, cruising.
July 19, 2000 visit - Hannah “spoke well” was “alert and active,” with regular bowel movements and good sleeping habits.
July 19, 2000 visit – Hannah received 9 vaccines:
D-T-aP, M-M-R, Hib, Varivax, and Polio
Followed by fevers, rashes, and descent into ASD.
https://web.archive.org/web/20170421045001/http://shodhganga.inflibnet.ac.in:80/bitstream/10603/12850/5/05_preface.pdf
All mercury compounds are toxic to humans and animals, but the organic forms, particularly methylmercury and dimethylmercury, have the highest toxicity. Methylmercury is the form found most widely in nature, and it bioaccumulates in the food chain. It is the form to which most human exposure occurs. Mercury has potent compromising effects upon the immune system and is also associated with chronic overgrowth of Candida, anemia, forgetfulness, tremors, depression, drowsiness, insomnia, headache, loss of energy etc. Chronically its toxicity causes low body temperature, bleeding gums, loosening of teeth and other mouth sores, sore throat, joint pain, high blood pressure, nutritional disturbances, urinary disturbances etc, to list just a few of the 42 conditions identified. Mercury poisoning is involved in five categories of pathology.
1) Neurological diseases.
2) Cardiovascular diseases.
3) Collagen diseases.
4) Immunological diseases.
5) Allergies.
GLUTATHIONE:
Sulfur-based protein that binds with heavy metals, viruses and toxins to eliminate them from system.
Very powerful fighter against oxidative stress.
Critical for protecting mitochondrial membranes from permeation/damage caused by toxins.
Tylenol blocks glutathione production in the liver.
AUTISM SPECTRUM DISORDER (ASD) kids have low or depleted levels of “thiols,” including glutathione.
Thiols are mercaptans, Latin for “capturing mercury.”
Targeted nutritional intervention with Folinic acid, and Betaine resulted in significant improvement in ASD children.
Addition of methyl B-12 to “cocktail” brought all ASD children within normal “thiol” levels, such as glutathione.
Thimerosal damage to nerves was associated with glutathione depletion, protection was restored with glutathione precursors.
AND SO ON AND SO FORTH
AND YET THEY HAVE THE AUDACITY
- TO CALL THESE ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VACCINATION “ANECDOTAL.”
- THOSE CONCERNED AS “POPULAR SCIENCE BLOGGER EPIGIRL,” THOSE “CLOSELY ASSOCIATED WITH THE ‘NATURAL MEDICINE MOVEMENT’” OR “SOME AFRICAN-AMERICAN PARENTS.”
- THOSE AFFECTED BY VACCINES AS “PEOPLE IN HIGH-RISK POPULATIONS, INCLUDING THOSE WITH OTHER MEDICAL CONDITIONS.”
AND THEY SIMPLY DISMISS THE FACT THAT THESE ADVERSE EFFECTS ARE RELATED TO RECEIVING THESE TOXIC INJECTIONS.
“Due to the small number of these cases, the significance of their association with Corovax was never determined As of this writing in 2030, longitudinal studies initiated by the NIH at the beginning of the vaccination program have not reached the next round of data collection, so formal analysis on these symptoms has not yet been conducted. Furthermore, these cases arose from the initial cohort of vaccine recipients—those in high-risk populations, including those with other underlying health conditions—making it increasingly difficult to determine the extent to which these symptoms are associated with vaccination.”
SO, WHO ARE THE “SCIENTISTS” WHO ALREADY KNEW THAT THESE NANOPARTICLES AND OTHER TOXIC SUBSTANCES IN THESE INJECTIONS ARE NON-TOXIC?
Back in October, a round table discussion called "Event 201" took place in New York. It featured global business, health and environment representatives
(including the World Health Organization and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention)
participated in an exercise on how to respond to a simulated pandemic, a fictional scenario very similar to the current one.
The participants in the live simulation represent a range of backgrounds and industries and include:
Latoya Abbott, Risk Management/Global Senior Director Occupational Health Services, Marriott International
Stan Bergman, Chairman and CEO, Henry Schein
Sofia Borges, Senior Vice President, UN Foundation
Chris Elias, President, Global Development division, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
Tim Evans, Former Senior Director of Health, World Bank Group
George Gao, Director-General, Chinese Center for Disease Control
Avril Haines, Former Deputy Director, Central Intelligence Agency; Former Deputy National Security Advisor
Jane Halton, Board member, ANZ Bank; Former Secretary of Finance and Former Secretary of Health, Australia
Matthew Harrington, Global President and Chief Operations Officer, Edelman
Chikwe Ihekweazu, Director General, Nigeria Centre for Disease Control
Martin Knuchel, Head of Crisis, Emergency and Business Continuity Management, Lufthansa Group Airlines
Eduardo Martinez, President, The UPS Foundation
Stephen Redd, Deputy Director for Public Health Service and Implementation Science, US CDC
Paul Stoffels, M.D., Vice Chair of the Executive Committee and Chief Scientific Officer, Johnson & Johnson
Hasti Taghi, Vice President and Executive Advisor, NBCUniversal Media
Lavan Thiru, Chief Representative, Monetary Authority of Singapore
https://centerforhealthsecurity.org/our-work/tabletop-exercises/event-201-pandemic-tabletop-exercise
The Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security in partnership with the World Economic Forum and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation…
…
Lo and behold
https://medalerts.org/vaersdb/findfield.php?TABLE=ON&GROUP1=SYM&EVENTS=ON&VAX=COVID19
Acute myocardial infarction 3,474 0.22% Arrhythmia 16,871 1.06%
Blood pressure increased 15,093 0.95%
Bradycardia 2,918 0.18% Cardiac discomfort 1,581 0.1% Cardiac disorder 2,940 0.18% Cardiac failure 3,612 0.23% Cardiac failure acute 677 0.04% Cardiac failure chronic 208 0.01% Cardiac failure congestive 1,649 0.1% Cardio-respiratory arrest 1,465 0.09% Cardiovascular disorder 2,020 0.13%
Cerebrovascular accident 10,172 0.64%
Chest discomfort 30,635 1.92% Chest pain 54,855 3.44%
Deep vein thrombosis 9,515 0.6%
Dizziness 125,466 7.86% ETC.































😉💯👍👏👏...Aaaannd then add the fact that glutathione a major endogenous antioxidant, is made up of glycine, glutamate and cysteine amino acids, and glysophate SUBSTITUTES for GLYCINE. 🤔😐😐
So one would not be able to MAKE the glutathione needed to remove a lot of toxicants that come into the body, and then the result is overloaded kidneys, liver, and the organs domino from there.
Combine that with nanoparticulates, especially those that can move past the BBB, along with heavy metals like Aluminium used in shots and many environmental exposures, and you have a perfect $#!@ storm for Autism and many other neurological disorders and organ overload symptoms.😐😐🤦♀️🤦♀️🤐
But yeah, "we" don't know why, and these chemicals/technology are GRAS or (never get tired of this one), perfectly "safe and effective".🤔🤔😤😤😤😤😐🤦♀️
#neverletthemforget #wearemany #wearememory #wewillnotforget #wewillnotforgive #mistakeswereNOTmade #getlocalised
> July 19, 2000 visit – Hannah [Poling] received 9 vaccines: D-T-aP, M-M-R, Hib, Varivax, and Polio
Injecting a combo of NINE known toxins (this is the intended function of these preparations) in order to unbalance the body (this is the intended and expected result of these injections) of a small child - without a single scientific justification, with the only premise of injuring the natural and functioning defenses of the body (aka eliciting immunological reaction), without a single document proving the safety of this combination…
This one act is the proof that a) administering doctors have lost their minds (with all due respect to their education and other medicine-related efforts), b) parents are misled and not informed enough, c) medicine, in particular pediatrics and virology, is no longer a valid science.
Besides, combining these nine known toxins into one visit must have been authorized or recommended by some higher authority. Who did this? On what scientific grounds? Or was it an isolated freelance initiative of this particular doctor? If yes, why? On what scientific grounds?