A REAL-LIFE PICTURE OF ERYTHROCYTES TRAPPED IN THE FIBRIN MESHWORK OF A CLOT
https://web.archive.org/web/20211013173710/https://web.archive.org/web/20101205210702/http://www.albanylawjournal.org/articles/Morrison_0609.pdf THE UNMANNED VOYAGE: AN EXAMINATION OF NANOROBOTIC LIABILITY
Scientists at New York University (NYU) have recently developed the ability to insert a nanorobotic arm into DNA.59 Control over the arm is manipulated by placing it in different parts of the DNA, and the arm would be moved by a rotary device that is attached to the DNA, hence DNA signals would control the arm.60 Essentially, the DNA of a person is the “muscle” for the robotic arm, but the scientists can control the actions of the arm depending on where it is placed on the DNA.61 The arm has been called a “controllable device[],”62 which poses the question of how controllable is the arm when is it positioned on the DNA and supposedly powered by it.
In the United States, Carnegie Mellon has a NanoRobotics laboratory.78
78 NanoRobotics Laboratory @ Carnegie Mellon, Robotic Micro and Nano-Assembly, http://www.me.cmu.edu/faculty1/sitti/nano/projects/nanomanipulation/ https://web.archive.org/web/20170914020807/http://nanolab.me.cmu.edu/projects/nanomanipulation/
LIABILITY FOR NANOROBOT ERROR
However, the small size of these nanorobots may lead to a grey area where it may be impossible to determine liability.89
The size of the components will create difficulty in determining where the error originated.90
The question will arise whether the manufacturer, designer, or doctor failed.
Working with nanoproducts is unpredictable since the size results in unusual properties beyond the normal laws of physics.91
The FDA has conceded that nanomaterials “have chemical or physical properties that are different from those of their larger counterparts.”92
This discussion is devoted to the grey area.
While in most cases it will be clear where fault lies and the proper action will be taken against the proper party, there will be ambiguity when exceptional cases arise as to determining causation.93
93 RESTATEMENT (SECOND) OF TORTS § 5 cmt. a (1965) (stating that while a person may be subject to liability, he may escape it if causation cannot be proven).
https://web.archive.org/web/20060813144820/http://www.fda.gov/bbs/topics/NEWS/2006/NEW01426.html
Therefore, the person who may most easily act to prevent or reduce harm must do so.96
93 RESTATEMENT (SECOND) OF TORTS § 5 cmt. a (1965) (stating that while a person may be subject to liability, he may escape it if causation cannot be proven).
96 See id. § 5.
It will be important to delineate the responsibilities between the doctor and the manufacturer in the use of nanorobots to determine which player has control over the device and is best suited to mitigate harm.
patient injury may be the only way of detecting error.
“The doctor must always be able to ‘pull the plug’108 on the nanomachines. This is one of the most important design constraints, one that will probably become a strict and universal regulatory requirement for all medical nanodevices.”109
Holding doctors responsible for monitoring the actions of the nanorobot may classify improper monitoring as an omission.110
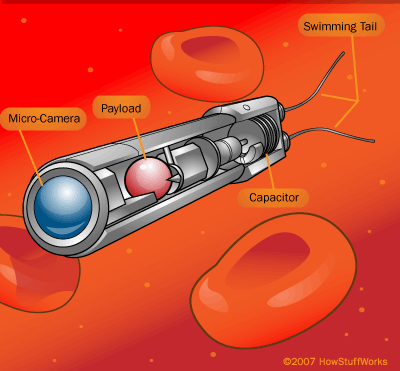
Sensors are an obvious method of controlling the nanorobots, and they can be used not only to determine the whereabouts and activity of the robot but to guide its actions as well.111 The methods that have been suggested for monitoring the robots may be impracticable, including a television camera allowing the doctor to steer the robot, which would require very complex sensors.112
All of the methods mentioned to control the device do not appear to actually control the actions of the robot but instead direct the focus of the robot’s activity.113
Simple robots will be relatively autonomous in their actions since they will perform minor functions.114
When nanorobots become more complex, the hazards will be greater since machines are not capable of thinking on the spot like humans.117 However, by taking some of the control away from doctors, there will need to be another human agent to blame, predictably the manufacturers of the robots.118
Since the robots are meant to perform the complex tasks usually performed by doctors, it will be easier to blame those that construct the robots for their failure.
Difficulties arise if the nanorobots can use the body as a power source and stay in the body for an extended period, possibly a lifetime in some cases, as would be the case in cancer vaccines.122
It appears that as long as doctors have not been negligent, they will not be responsible for the failure of a device.
This makes it easier for doctors to attribute the causation of device error to the manufacturer.
Because the devices would be so small, how would we ever know? Since liability is unclear in the case of nanorobots, especially when considering their future designs and method of control are unknown, alternative methods of regulation and spreading the risk of liability should be created.
Nanorobotic technology in the medical field gives rise to liability issues for nanorobotic failure or error. A preventative measure would be for government agencies to implement regulations controlling the use of products containing nanotechnology.
While the FDA has an Office for Combination Products, this office does not create additional regulations for nanoproducts; instead it just determines which department is controlling.133 Ambiguity does not give rise to proper oversight, which leaves these nanorobots virtually unregulated.134 The current lack of regulations and guidance from the FDA has drawn criticism due to the peculiar nature of nanorobots and their potential abilities.135 The FDA has defined an example of a nanotechnology combination product as a “[m]ulti-component system that may consist of [a c]arrier/delivery system (drug or device)[or] . . . [t]argeting agent.”136
Numerous commentators have warned about the lack of formal regulation for nanoproducts.146 Mandatory post-market surveillance of all nanoproducts would be an effective way of not stifling innovation of nanotechnology, while ensuring safety in the products.
Government regulation of nanotechnology will be difficult, as the FDA has admitted150. There are myriad issues that will confront regulation of nanotechnology, including classification.151 The issue of whether there should be separate regulations for products that contain nanotechnology or whether the products should be governed under existing regulations is a topic of debate.152 Whether the federal government will adopt regulations for nanotechnology has yet to be seen. New regulations will be necessary since nanoproducts are innovative and the risks are not clear.153 While government agencies have emphasized their concern for safety regarding nanoproducts, they have not taken concrete steps to ensure such safety. Instead they have placed the burden elsewhere and in some cases, downplayed the risks.
However, the ultimate burden will truly rest with the designers and manufacturers of the products since they will be competing with other companies to have their products distributed.
Companies that distribute the products to the open market are unlikely to assume costs to ensure the safety of a product; instead they will mostly likely require assurances from the manufacturers before agreeing to sell the product. By placing the responsibility of ensuring environmentally friendly products on manufacturers and companies that distribute products, the EPA is less likely to be charged with lax regulation of nanoproducts. This is convenient for the government since the agencies may not have adequate funding to ensure the safety of nanotech products through research and testing.
Government agencies recognize that these products, while potentially beneficial, may be harmful as well. The EPA has acknowledged that the small size of nanoproducts may create novel risks.159
Other government agencies, such as the FDA, may soon follow suit in regulating nanotech products due to this awareness.160
However, regulation may be illusory, since it does not appear that the agencies want actually want to take proactive steps toward novel regulation tailored to nanotechnology; rather, agencies are trying to classify nanoproducts under existing regulations.
It appears that the nomenclature used to describe nanoproducts is going to be a fundamental aspect of classification and regulation.
The public scrutiny and justifiable suspicion toward nanotechnology should be taken into account when creating regulations. This requires “a proactive approach from the industry with clear and timely communication from all involved parties in order to correctly inform the public to the true measure of the risk associated with these products.”167 We must remember to keep in mind those that would be impacted the most by nanotechnology. The legal maxim that juries are important to provide representation of the public in legal trials has been translated to the nanotechnology field. Britain has implemented “NanoJuries” which consist of twenty people that give their views on information provided to them concerning nanotechnology for impacting policy.168 The FDA recognized the importance of public input by taking public comments and holding a public hearing on nanotechnology.169
VI. CONCLUSION
While it is impossible to predict the future, we may understand the consequences of adding nanorobots to the medical field by looking at experience with asbestos liability and the present growth of nanotechnology.
The liability of the potential myriad characters will be the cause of great confusion and debate.
The public may even accept the potential risk of nanotechnology related products to allow for the technology’s development and a better understanding of what policies are necessary.
The nanorobot designers may try to mitigate their fault by arguing there was strong public support through the nanojuries or other public comment.
It is essential not to take settled regulations and laws and apply them to a radically different phenomenon blindly.
However, if government agencies do not step up and try to control the litigation before it begins; other methods must be examined to limit tort liability.
In essence, if the government does not create regulations at some point, the litigation may come to a point that will put an extreme burden on the judicial system.
Do you think they don't know what is going on and why there are such adverse effects and deaths? Of course, they know, and they need to be held accountable!
Bacteria based
uses a flagellum for propulsion purposes
use similar mechanisms as the biological microorganisms
https://web.archive.org/web/20060904090507/http://howard.engr.siu.edu/mech/faculty/hippo/me465sp05jonespres.ppt Nanorobot Mechanocompatibility
https://web.archive.org/web/20081209070952/http://iete-elan.ac.in:80/sample-seminar.ppt
MEDICAL AREA
Nano surgical tools can help in making up the damages at molecular and cellular level.
Nanotechnology may also be useful for developing ways to detect and eradicate cancer cells.
Nanorobots could also be programmed to perform delicate surgeries or remove obstructions in the circulatory system.
SUPERCOMPUTERS
Assemblers will enable the construction of both molecular electronic and molecular mechanical devices. It is to be expected that electronic effects will permit faster switching times than do mechanical effects, permitting the construction of faster and much powerful computers.
MULTI-WALLED CARBON NANOTUBE
MICRO ELECTRO-MECHANICAL SYSTEM (MEMS)
Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) is the integration of mechanical elements, sensors, actuators, and electronics on a common silicon substrate through micro fabrication technology. While the electronics are fabricated using integrated circuit (IC) process sequences (e.g., CMOS, Bipolar, or BICMOS processes), the micromechanical components are fabricated using compatible "micromachining" processes that selectively etch away parts of the silicon wafer or add new structural layers to form the mechanical and electromechanical devices.
On the other hand, the introduction of large quantities of nano structured materials into our society may have unforeseen consequences for environmental quality.
Disadvantages of Nanotechnology
Nanotech particles will penetrate living cells and accumulate in animal organs and can perhaps enter the food chain.
There is no regulatory body dedicated to check this potent and powerful invasion
Their impact on environment is unknown. e.g. Nanotubes of carbon use gallium & arsenic and minute traces of gallium arsenide in the body could prove toxic
Changes in the proteins due to the presence of nano particles in the blood stream could trigger dangerous effects like blood clotting
A whole new class of toxins or the environmental problems may be created due to nanotechnology.
Reaction of humans and existing environment to these nanoparticles and nanobots and their acceptance is not known.
Nanotechnology is slowly but steadily ushering in the new industrial revolution.
https://web.archive.org/web/20060918012802/http://howard.engr.siu.edu/mech/faculty/hippo/me465sp05dunmyerpres.ppt Systemic Nanorobot Distribution and Phagocytosis
Trapping in the Liver
Is fourth highest specific blood perfusion rate, typically 1000-1400 cm3/min.
Injection of 15 and 80 micron microspheres directly into the portal vein in rat liver induce embolic portal hypertension. – This is bad
Trapping in the Spleen
Is third highest specific blood perfusion rate, typically 450 cm3/min.
Probably most likely site where trapping may occur.
Serves as a sieve or filtration bed. It gathers deformed, malformed cells such as “sickled” cells.
Trapping in the Kidney
Is second highest specific blood perfusion rate, typically 1300 cm3/min.
In Cats microspheres 300, 1800, and 3500 nm were readily passed through feline kidney.
In Rats 8000 to 12000 nm microspheres were completely extracted from the blood stream.
Trapping in the Lungs
Highest specific blood perfusion rate, typically 4500 cm3/min.
Radiolabeled microspheres administered to a Beagle Dog showed that 8000 to 25000 nm spheres stayed in the lung at least one month.
3000 nm spheres rapidly cleared from the lungs and appeared in the Liver and Spleen after a month.
How to Avoid Phagocytosis
Most Bacteria are successful at avoiding phagocytes by interfering with the methods of phagocytosis or avoiding them completely.
Estimates show it is apparent that every medical nanorobot injected in to the body will physically encounter a phagocyte many times during its mission.
Nanorobots could carry surface recognizers that designate the robot as “self”
Chemorepulsion might work however it could disrupt normal immune systems.
Inhibiting by moving out of the way.
Removing it self from the phagocyte by rupturing it – however may be harmful if done continuously.
Will free nanoparts be cytotoxic or possibly systemically toxic.
For diagnostic purposes, parameters like diff gradients on temperature, concentration of chemicals in bloodstream and electromagnetic signals are concerned
CMOS VLSI systems design using deep ultraviolet lithography provides high precision for manufacturing nanodevices and nanoelectronics systems
The joint use of nanophotonic and nanotubes may provide resolution ranging from 248nm to 157 nm devices
VHDL become most common in IC manufacturing industry
Mobile phones are used for retrieving information about patient conditions and current status of nanorobots
New materials like strained channel with SiGe layer can reduce self heating and improve performance
Silicon On Insulator technology is used to assemble high performance sub 90nm circuits
This solves problems such as bipolar effect and hysteretic variations arising in Circuit design
RF based telemetry gives good results in patient monitoring and power transmission
It uses RFID CMOS which allows track information about the nanorobot position
Nanorobotic Communication
One of the simplest ways to send broadcast type messages into the body, to be received in vivo nanorobots, is acoustic messaging.
A device similar to an ultrasound probe would encode messages on acoustic carrier waves at frequencies between 1-10 Mhz. Thus the supervising physician can easily send new commands to nanorobots already at work inside the body.
The other half of the process is getting messages back out of the body, from working nanodevices out to the physician. It is convenient to establish an internal communications network that can collect local messages and pass them along to a central location, which the physician can then monitor using sensitive ultrasound detectors to receive the messages.
A navigation network may be installed in the body, with station keeping navigational elements providing high positional accuracy to all passing nanorobots that interrogate them, wanting to know their location.
The “Respirocyte”
An artificial mechanical red cell which measures about 1 micron in diameter and floats along in the bloodstream.
It is a spherical nanorobot made of 18 billion atoms.
The reciprocyte is essentially a tiny pressure tank that mimics the action of the natural hemoglobin-filled red blood cells.
Reciprocytes will have pressure sensors to receive acoustic signals from the doctor, who will use an ultrasound-like transmitter device to give the reciprocytes commands to modify their behavior while they are still inside the patient’s body.
Virus “Finders”
Floating in an aliquot of laboratory test fluid, these hypothetical early medical nanorobots are testing their ability to find and grasp passing virus particles.
The incompetence or negligence of medical personnel is always a potential concern.
The most serious problems may devolve from inherent complexity of a trillion machines independently trying to cooperatively work on a very complex repair problem in a short period of time.
One class of malfunction might involve some unexpected emergent machine-machine interaction.
TOXICITY? NAH…
http://playppt.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/Nano-Robotics-PPT.pptx NANOROBOTICS
They are intelligent robots that store enormous amounts of information, like vaccines and antidotes for illnesses
Medical Micro/Nanorobots in Precision Medicine
https://web.archive.org/web/20180723154420/https://cnnt-pucioasa-nanochannels.wikispaces.com/file/view/Nanotechnology.%20Marisoiu%20Marius.pptx/305080486/Nanotechnology.%20Marisoiu%20Marius.pptx Nanotechnology and Medicine
Manipulating material at a scale of individual atoms and molecules
Imagining the whole Encyclopedia Britannica written on head of a pin at IBM in the US, a technique called electron beam lithography was used to create nanostructures and devices as small as 40 to 70 nm in the early 1970s
Nanotechnology is a new field with many possible uses, medicine being one of them
“The manufacturing technology of the 21st century"
“A single inhaled nanorobot reaches, deeply inspired into the lungs, enters an alveolar duct and attaches to the tissue surface.”
Although the future of medicine lies unclear, it is certain that nanotechnology will have a significant impact.
CONSTRUCTION
SOURCES OF ENERGY
Glucose / natural body sugars / body heat and oxygen and other biochemical / molecular parts.
By using the energy & mass in the body the nanorobots can replicate themselves to ‘n’ times.
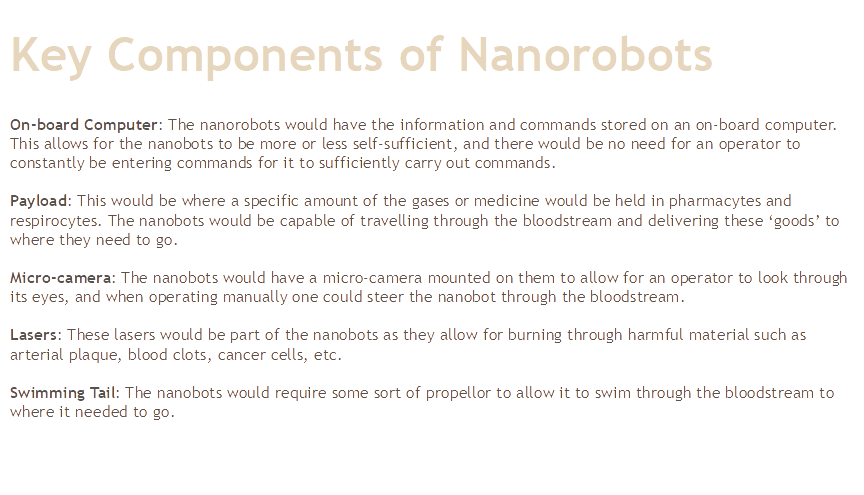
FEATURES OF NANOROBOT
Nanorobot posses at least rudimentary two way communication.
It will response to acoustic signals.
It will able to receive power and programming instructions from external source via sound waves.
A patient undergoing this treatment could expect to have no awareness of molecular devices working inside him.
DRILLERS,PEEPERS,STRINGERS ENGAGE IN A DELICATE
SURGICAL OPERATION TO REMOVE A CANCER TUMOUR.
We can monitor and control the nanorobots by programming.
https://web.archive.org/web/20060904090029/http://howard.engr.siu.edu/mech/faculty/hippo/me465sp05rayfordpres.ppt Communication of Nanomedical Devices
Nanorobot Communication Requirements
Definition of Nanomachine
1.) Coordinate complex, large-scale cooperative activities,
2.) Pass along relevant sensory, messaging, navigational, and other operational data, and
3.) Monitor collective task progress.
Communication Modalities
Any method by which materials or power can be transferred into, around, or out of the human body also may be employed as a mode of communication by imposing a time-varying modulation on the flow. For in vivo communications, most common modalities are: free-tissue chemical, acoustic, electromagnetic broadcast, nanomechanical and cable systems, and dedicated communicytes.
Communication Tasks
Nanomedical messaging tasks fall into three broad categories:
1. nanorobots communicating with externalities including
physicians, laboratory machines, external computers,
or even the conscious perception of the patient him/herself;
2. nanorobots communicating with other nanorobots; and
3. nanorobots communicating with human organs, tissues, or cellular systems.
Types of Inmessaging
Inmessaging from External Sources: Chemical, Acoustic, Electromagnetic, Cable Inmessaging and Message Depots, Eavesdropping, and Macrosensing
Inmessaging from Patient or User
Can Nanorobots stationed inside one patient communicate with nanorobots stationed inside another patient?
Extracorporeal contacts through communicyte exchange
Data is readily transferred purposely between patients
http://www.123seminarsonly.com/Seminar-Reports/039/37621303-Nanorobotics.pptx
https://web.archive.org/web/20180422021649/http://web.iitd.ac.in:80/~achugh/Lecture%208.pptx
“The entire cell can be viewed as a factory that contains an elaborate network of interlocking assembly lines, each of which is composed of a set of large protein machines…. Why do we call the large protein assemblies that underline cell function protein machines? Precisely because, like machines invented by humans to deal efficiently with the macroscopic world, these protein assemblies contain highly coordinated moving parts” - Bruce Alberts, Cell 92, 291 (1998).
Self replicative such as prions
Nanotoxicity
Immunological reaction
Biocompatibility
Biodistribution
Lack of evaluation systems
https://web.archive.org/web/20201016164616/https://15cd0654-a-52c2874a-s-sites.googlegroups.com/feeds/media/content/ctyi.org/cutting-edge-science-2015/4626956303698796732 Medical Applications of Nanorobotics
A navigational network may be installed in the body, which may provide high positional accuracy to all passing nanorobots
This will enable the physician to keep track of the various devices in the body
Application of Nanotechnology in Medicine
Diagnostic
- Imaging
- Quantum dots
- Microscopic sampling
Detection of airway abnormalities
Therapeutic
Delivering medication to the exact location
Killing of bacteria, viruses & cancer cells
Repair of damaged tissues
Oxygen transport
Skin and dental care
Augmentation of immune system
Treatment of Atherosclerosis
The clottocyte concept
Brain enhancement
Diagnostic Applications of Nanotechnology in Medicine
Another way to use nanotech as tracking devices is to use “quantum dots”
These tiny semiconductors are able to emit wavelengths of light (colors) that depend on their size. If quantum dot A is twice as big as quantum dot B, it will emit a different color.
Quantum dots are better than conventional dyes:
They last much longer
More colors can be made available.
Medical nanodevices could augment the immune system by finding and disabling unwanted bacteria and viruses.
CLOT-INDUCING MEDICAL NANOROBOTS ARE SHOWN IN VARIOUS STAGES OF CLOT-NETTING DEPLOYMENT.
MEDICAL NANOROBOTS WITH FULLY DEPLOYED NETTING ARE SHOWN EMBEDDED IN A PATCHLIKE GROWING CLOT WITH RED CELLS AND FIBRIN STRANDS INVOLVED.
❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗
👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆
CLOT-INDUCING MEDICAL NANOROBOTS WITH FULLY-DEPLOYED NETTING ARE SHOWN EMBEDDED IN A PATCHLIKE GROWING CLOT WITH RED CELLS AND FIBRIN STRANDS INVOLVED (A CLOSER LOOK)
A REAL-LIFE PICTURE OF ERYTHROCYTES TRAPPED IN THE FIBRIN MESHWORK OF A CLOT
Injection of magnetic particles that binds to cancerous cells
Heating the particles b/w 1`C and 5`C with a light oven…
NANO WIRES
CANTILEVERS
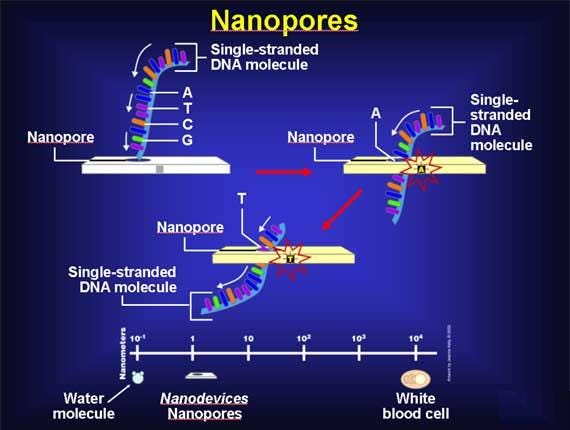
NANO PORES
NANO SHELLS
DENDRIMERS
NANOTUBES
Control Wireless Device Inside Artery http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2007/03/070319113137.htm
Nanorobot Immunoreactivity
The immune system is the first line of defense which consists of complex organs.
It is with these organs foreign matter is detected and reacts to this foreign matter.
This is the key to measuring biocompatibility inside the human body.
Human Immune System Response
Nonspecific immune response reacts within a few minutes to challenges.
Specific immune response is a learned or adaptive system that is slow acting (5-7 days depending upon the type of infection).
Complement Activiation
Consists of a 20 plasma and cell membrane proteins which is synthesized by the liver and macrophages (cells within the immune system).
Nanorobots could potentially activate complement causing cell death, shock, and stimulation of the autoimmune-type response.
Tolerization: Nanorobots introduced into the newborn may train the neonatal immune system to regard these foreign materials as “native.”
Colonel Deletion: Once the paratopes of antibodies that bind to the nanorobots are determined, immunotoxin molecules can be engineered and then injected into the patient.
Inflammation & Allergic Reactions
Inflammation occurs when tissue damage including trauma, infection, cell death, and intrusion of a foreign material.
Allergic hypersensitivity is the most common disorder of the immune system.
Occurs when an individual is exposed to an allergen and develops a sensititivity.
Conclusion
Biocompatibility is the most important aspect in choosing material for medical devices and/or applications.
There are various types of biomaterials and testing procedures for these materials.
The human body will interact with nanorobots possibly causing adverse reactions.
❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗❗
👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆👆
Nanotechnology is a hybrid science combining engineering and chemistry. Atoms and molecules stick together because they have complementary shapes that lock together, or charges that attract. Just like with magnets, a positively charged atom will stick to a negatively charged atom. As millions of these atoms are pieced together by nanomachines, a specific product will begin to take shape. The goal of nanotechnology is to manipulate atoms individually and place them in a pattern to produce a desired structure.
Nanorobots could also be programmed to perform delicate surgeries -- such nanosurgeons could work at a level a thousand times more precise than the sharpest scalpel. By working on such a small scale, a nanorobot could operate without leaving the scars that conventional surgery does. Additionally, nanorobots could change your physical appearance. (cont.)
They could be programmed to perform cosmetic surgery, rearranging your atoms to change your ears, nose, eye color or any other physical feature you wish to alter.
Problems/Risks
Technological Singularity
- Artificial intelligence
Cheaper, more destructive weapons
- Self-replicating Weapons of Mass Destruction
III. Parasitic Nanorobots
1. Self-replicating nanorobots may consume raw materials without concern
2. Guidelines are established to prevent “free-foraging self-replicating pseudo-organisms on the Earth's s
Dangers
1. Weapons
2. Virus and bacteria
Conclusions
Molecular nanotechnology has a very high potential future and widespread applications.
Although potentially useful, it can also be potentially dangerous.
It has become appallingly obvious that our technology has exceeded our humanity.
- Albert Einstein
such nanosurgeons could work at a level a thousand times more precise than the sharpest scalpel…
They could be programmed to perform cosmetic surgery, rearranging your atoms to change your ears, nose, eye color or any other physical feature you wish to alter.
Patients will drink fluids containing nanorobots programmed to attack and reconstruct the molecular structure of cancer cells and viruses to make them harmless. There's even speculation that nanorobots could slow or reverse the aging process, and life expectancy could increase significantly. (cont.)
In 2005, Brad Nelson’s team reported the fabrication of microscopic robot small enough to be injected into the body hoping that this device and its descendants might be used to deliver drugs.
https://web.archive.org/web/20231020054434/https://fui.edu.pk/fjs/index.php/fujeas/article/download/381/265 Nanotechnologies: AI Weapons Governing the Military Battle Field
…

































































































The ultimate burden will always be borne by the PATIENT.
This is nearly impossible to read, it is such a psychopathic gruel brew. Where are the brakes to all of this self assembly? Once let loose into the environment. No wonder they hoarded seed and gene banks (Svalbard) years ago. That describes the whole experiment, unsanctioned by the test subjects, but built under our noses and given “silent consent. “
Why am I thinking "Do we really need this stuff?" I have no plans to ever have any of this stuff near me. I like natural...healing with food and natural stuff. The world of nano seems insane to me.